Home >> Optics, prisms
deviation |
|
Deviation
Deviation, measured in degrees, is the angle an incident ray is turned through after passing through a prism(or other optical component).
This deviation is a minimum for a prism when the path of a light ray is symmetrical about its axis of symmetry.
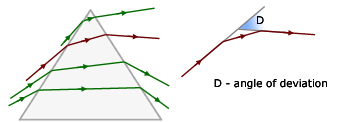
Derivation of Minimum Deviation D
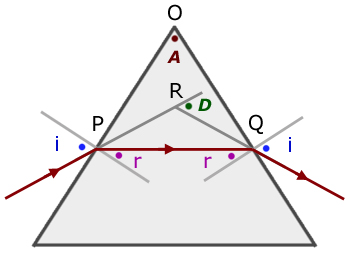
In ![]()
![]() (i
(i
(D external angle of ![]() )
)
around points P and Q respectively,
![]()
![]()
substituting into equation (i
![]() (ii
(ii
In ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() (iii
(iii
adding together equations (ii & (iii,
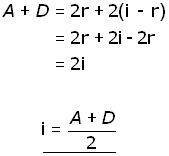 (iv
(iv
rearranging equation (iii,
![]() (v
(v
Using Snell's Law equation,
![]()
and substituting for i and r from equations (iv & (v above,
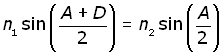
n1 is the refractive index of air which approximates to 1. Hence the equation becomes:
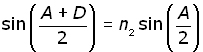
Example
So for a 60o equilateral prism made of glass(n = 1.5 approx.), the minimum deviation angle D is given by:
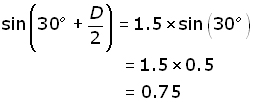
It follows that:
![]()
remembering that sin-1(x) means the angle whose sine is 'x',
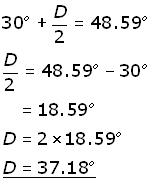
Chromatic dispersion
The term Chromatic dispersion describes how refractive index changes with wavelength for a particular medium.
Medium |
Violet |
Red |
Crown glass |
10.00 |
10.37 |
Acrylic |
10.46 |
10.87 |
Fused quartz |
11.30 |
11.58 |
data courtesy of Serway & Jewett
Using refractive index theory we can formulate equations in terms of the wavelength of the light involved:
Remembering that: nm is defined as the absolute refractive index
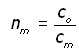
where,
co is the velocity of white light in a vacuum
cm is the velocity of white light in the medium
It follows that: nv is defined as the absolute refractive index for violet light
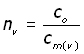 (i
(i
where, cm(v) is the velocity of violet light in the medium
Similarly, nr is defined as the absolute refractive index for red light
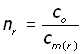 (ii
(ii
where, cm(r) is the velocity of red light in the medium
Since frequency f is constant throughout,
![]()
and
![]()
where,
λo is the wavelength of white light in a vacuum
λm(v) is the wavelength of violet light in the medium
λm(r) is the wavelength of red light in the medium
Substituting for cm(v) , cm(r) and co into equations (i and (ii ,
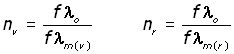
cancelling f in each equation,

Minimum angle of dispersion
This is measure of the angle of 'spread' of a spectrum when it leaves a prism. For minimum angular dispersion, the angle is derived from the difference in deviation between red and violet rays of light.
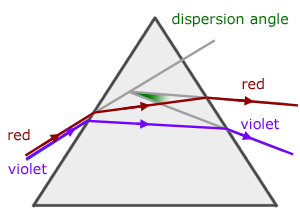
Replacing n2 with nr for red, and nv for violet light in the minimum deviation equation below,
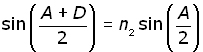
we can calculate values of deviation for each colour. Subtracting the angles gives the minimum dispersion angle for white light.
[ About ] [ FAQ ] [ Links ] [ Terms & Conditions ] [ Privacy ] [ Site Map ] [ Contact ]
