Home >> Thermal, gas laws
Boyle's law |
|||
Boyle's Law
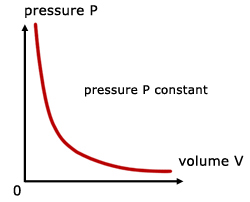
For a fixed mass of gas at constant temperature and pressure, the pressure is inversely proportional to the volume.
![]()
making the proportionality into an equality,
![]()
where k is a constant
Now, consider a fixed mass of gas at one temperature at different pressures and volumes,
![]()
elimenating the constant k
![]()
Charles' Law
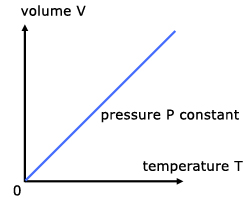
For a fixed mass of gas at constant temperature and pressure, the volume is directly proportional to the temperature(K).
![]()
making the proportionality into an equality,
![]()
where m is a constant
![]()
Now, consider a fixed mass of gas at one pressure at two different temperatures and volumes,
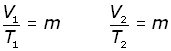
elimenating the constant m,
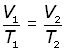
Pressure Law
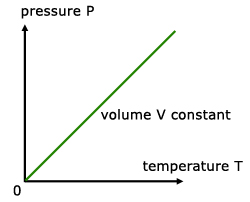
For a fixed mass of gas at constant temperature and pressure, the pressure is directly proportional to the temperature(K).
![]()
making the proportionality into an equality,
![]()
where n is a constant
![]()
Now, consider a fixed mass of gas at one volume at two different temperatures and pressures,
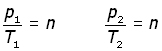
elimenating the constant n,
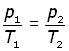
Combined gas equation
The three gas law equations, with constants k,m,n are :
![]()
![]()
![]()
These can be combined into one equation:
![]()
where K is a new constant
Now, consider a fixed mass of gas at two different temperatures, volumes and pressures,

elimenating the constant K,
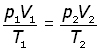
The Mole(mol)
A Mole is the amount of substance that has the same no. of particles as there are atoms in 12g of carbon 12.
or
A Mole of anything contains the Avagadro number of particles.
Avagadro's Number (NA) = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1
A Mole is a very large number.
Consider the Earth's population at present 6 x 109. A Mole of people would be equivalent to 1014 Earths !
The mass of one mole of a substance is the relative molecular mass(RMM) of a substance expressed in grams.
eg 1 mole of molecular hydrogen (H2) has a mass of 2g
The Ideal Gas Equation
The combined gas equation,
![]()
can be modified to take account of the amount of gas in units of moles. This is done by making the constant K a function of the number of moles n of gas present .
![]()
R is the Universal Gas Constant (= 8.31 JK-1mol-1 )
The 'equation of state' for an ideal gas is then given by:
![]()
An 'ideal gas' is not a perfect model, but it is a good approximation.
The concept is based on the assumption that gas internal energy is only kinetic in nature.
The equation is accurate for real gases at low pressures and at temperatures well above liquefaction.
Units
V - volume cubic metres m3
p - pressure Pascals Pa (1 Pa = 1 Newton per square metre)
T - temperature Kelvin K
[ About ] [ FAQ ] [ Links ] [ Terms & Conditions ] [ Privacy ] [ Site Map ] [ Contact ]
