Home >> Fields, gravitational fields 3
Kepler's laws #1 |
derivation of Kepler's 3rd law from Newton's Law of Gravitation |
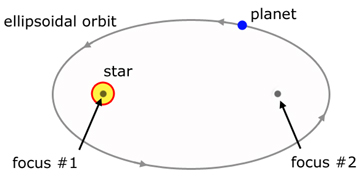
Kepler's 1st. Law - The Orbit Law
The orbit of a planet is in the shape of an ellipse, with the parent star at one focus.
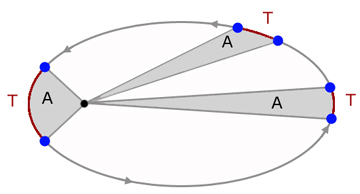
Kepler's 2nd. Law- The Area Law
A planet moves such that an imaginary line between it and the parent star sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
Kepler's 3rd. Law - The Period law
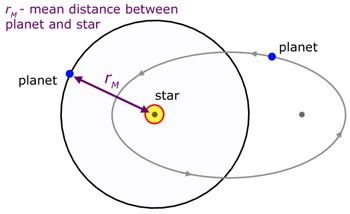
The square of the orbital period of a planet is proportional to the cube of the mean distance to its parent star.
T - orbital period
rM - mean distance
![]()
table
Kepler's 3rd law derived from Newton's Law of Gravitation
The centripetal force F keeping a mass m in orbit is given by:
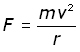
The angular velocity ω is the angle (in radians) traced out when the mass travels v metres in one second. Stating this definition in an equation and making v the subject:
![]()
Substitung for v into our equation for centripetal force:
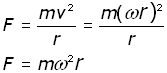 (i
(i
The centripetal force is provided by gravity.
Hence,
![]() (ii
(ii
Equating equations (i and (ii ,
![]() (iii
(iii
The period T of the orbital motion is the circumference (in radians) divided by the angular velocity. Making ω the subject of the equation:
![]()
and substituting for ω into equation (iii
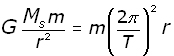
We obtain the expression:
![]()
Now making T 2 the subject:
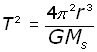
If we now remove the constants G MS π by making the equation a proportionality:
![]()
Hence Kepler's 3rd Law is consistent with Newton's Law of Gravitation.
[ About ] [ FAQ ] [ Links ] [ Terms & Conditions ] [ Privacy ] [ Site Map ] [ Contact ]
