Home >> Optics, total internal reflection
critical angle |
Critical Angle
The Critical Angle (co)is the angle of incidence in a dense medium, such that the angle of refraction in the less dense medium is 90o .
Looking at the diagrams(below), as the angle of incidence in the dense medium is increased, the angle of refraction increases towards 90o. During this time a weak reflected ray is also observed.
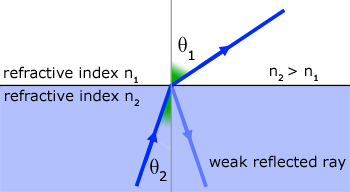
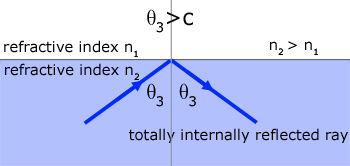
Only when the angle of incidence in the medium exceeds the Critical Angle does all the light become reflected internally.
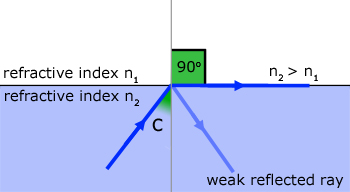
We can formulate an equation for the critical angle using Snell's Law for two media of refractive index n1 & n2 .
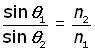
![]()
When θ1= 90o and θ2= co ,
![]()
but sin(90o) = 1, therefore:
![]()
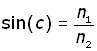
from work on relative refractive index,

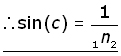
90odeviation with a 90o prism
Total internal reflection in glass depends on the fact that its critical angle is approximately 42o . A light ray with an angle of incidence greater than this will be totally internally reflected. So a light ray with an angle of incidence of 45o will be reflected, and its angle of reflection will also be 45o. Hence the light ray is deviated through an angle of 90o .
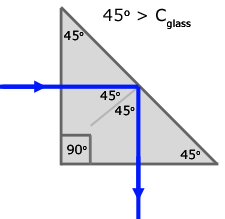
For 90o deviation, a 90o isosceles glass prism is used. In this way the incident ray and the reflected rays are normal to the surfaces they enter and leave(and therefore unhindered). Total internal reflection occurs on the hypotenuse.
180odeviation with a 90o prism
Besides a 90o deviation, an isosceles prism is also used to produce a 180o deviation, but this time reflection occurs on the equal, adjacent sides of the prism and not on the hypotenuse.
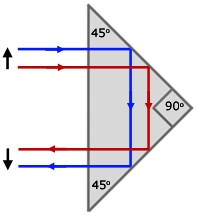
By tracing two light rays though the prism, it can be seen that the image produced is inverted. As a result of the image being reflected twice, lateral inversion is cancelled.
Optical fibres
Optical fibre typically consists of a core of high refractive index surrounded by cladding with a lower refractive index. Light is totally internally reflected down the fibre at the boundary of the two media.
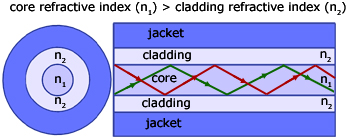
Optical fibre has a number of advantages over copper wire:
1. less attenuation
2. cheaper metre for metre
3. can carry more information
4. immune to electrical interference
5. safer - no fire risk as with electric currents
6. wire-tapping more difficult
[ About ] [ FAQ ] [ Links ] [ Terms & Conditions ] [ Privacy ] [ Site Map ] [ Contact ]
