Home >> Optics, plane mirrors
laws of reflection |
Laws of Reflection
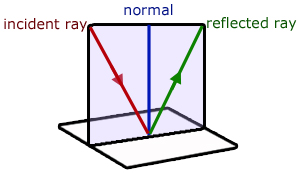
1. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal, at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
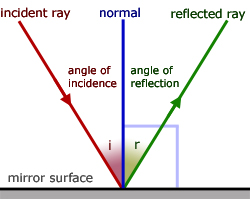
2. The angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence
Hence an image can be located by taking two light rays from a point object and retracing them after reflection.
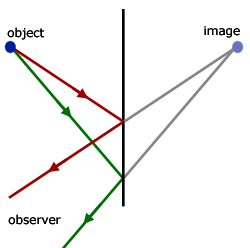
Plane mirror images
1. All images are virtual. That is, they cannot be projected on to a screen.
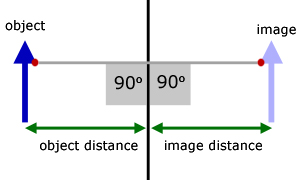
2. The image produced in a mirror is as far behind the mirror as the object is infront.
object distance = image distance
3. The image is the same size as the object.
4. A line joining a point on the image to a corresponding point on the object is perpendicular to the mirror.
5. The image is laterally inverted (sideways upside down).

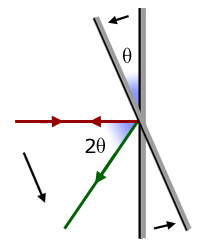
Mirror rotation
When a light ray is normal to a mirror it reflects back the way it came. However, if the mirror is tilted say, through θ o(theta) then the reflected light ray rotates through 2θ o .
[ About ] [ FAQ ] [ Links ] [ Terms & Conditions ] [ Privacy ] [ Site Map ] [ Contact ]
