Home >> Optics, refraction
laws refraction |
The Laws of Refraction
Consider a single light ray travelling through a low density material (eg air) and being refracted at the surface of a transparent material with higher density (eg glass).
The normal is a line drawn at right angles to the material's surface at the ray's point of entry.
The angle of incidence is the angle the light ray makes with the normal.
The angle of refraction is the angle the refracted light ray makes with the normal inside the material.
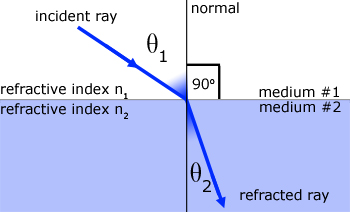
1) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of entry are all in the same plane.
2) The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant for a particular wavelength (Snell's Law).
The ratio constant is called the relative refractive index 'n' .
(older texts - the Greek letter 'μ' mu)
The relative refractive index between two media where a light ray travels through one medium (#1) and is refracted through the other medium (#2) is given by:
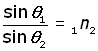
Refractive Index
The refractive index of a single medium can be defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium.
Here
nm is defined as the absolute refractive index
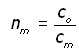
where,
co is the velocity of light in a vacuum
cm is the velocity of light in the medium
let us consider our two materials(#1 & #2 from above). Their absolute refractive indices are given by:

dividing the second equation by the first,
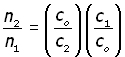
that is,
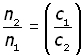
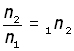
Snell's Law equation can now be rewritten as:
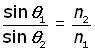
or
![]()
note: when a light ray travels from a less dense medium to a denser medium, it bends towards the normal(and vice versa).
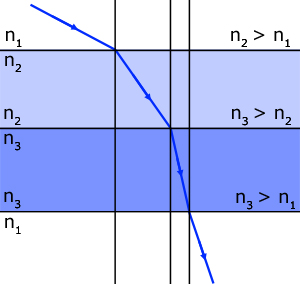
Common refractive indices
Material |
n (λ = 589.29nm) |
|
|---|---|---|
Water |
1.3330 |
|
Diamond |
2.419 |
|
Amber |
1.55 |
|
Fused silica |
1.458 |
|
Sodium chloride |
1.50 |
|
Liquid Helium |
1.025 |
|
Water ice |
1.31 |
|
Acrylic glass |
1.490 - 1.492 |
|
Polycarbonate |
1.584 - 1.586 |
|
Crown glass |
1.50 - 1.54 |
|
Flint glass |
1.60 - 1.62 |
|
Crown glass |
1.485 - 1.755 |
|
Flint glass |
1.523 - 1.925 |
|
Pyrex |
1.470 |
|
Cryolite |
1.338 |
|
Rock salt |
1.516 |
|
Sapphire |
1.762–1.778 |
|
Cubic zirconia |
2.15 - 2.18 |
|
Moissanite |
2.65 - 2.69 |
|
[ About ] [ FAQ ] [ Links ] [ Terms & Conditions ] [ Privacy ] [ Site Map ] [ Contact ]
