Home >> Nuclear, the nucleus
Revision
From intermediate physics you should know these rudimentary facts:
Three types of particles make up the general structure of an atom: electrons, protons & neutrons.
Neutrons and protons exist in the nucleus at the centre of the atom.
Electrons orbit around the nucleus in orbits.
The number of protons in a nucleus is called the atomic number Z.
The total number of protons & neutrons in a nucleus is called the mass number A.
In an electrically neutral atom, the numbers of protons equals the numbers of electrons.
Ions are electrically charged atoms, when an atom has more or less than the normal numbers of electrons.
Isotopes are forms of atoms of an element with differing numbers of neutrons in the nucleus.
The particles(nucleons) in a nucleus may be represented as:
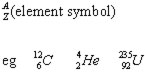
The Relative Atomic Mass Ar
This must not be confused with the mass unit A, which is the the number of nucleons(protons + neutrons) in the nucleus.
The relative atomic mass of an atom( Ar) is defined as:
![]()
So for a carbon atom this exactly equals 12 ( Ar=12).
One of these relative atomic mass units(sometimes called the unified atomic mass unit) is called 1u.
So carbon has a relative atomic mass of 12u .
The actually value of 1u can be measured experimentally by dividing the mass of a carbon atom ( 1.992 x 10-26kg) by 12.
1u = 1.660 x 10-27
Nuclear radii
The nucleus is much smaller than the atom. The radius of a nucleus is approximately 10-4 that of the atom it occupies.
The radius of a nucleus is proportional to cube root of the mass number(nucleon number) A.
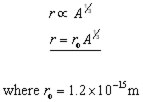
Nuclear density
The volume of a nucleus is approximately 10-12 that of the atom.
Since most of the mass resides in the nucleus, it follows that its density is extremely high. The nuclear density is approximately the same for all nuclei( 1017 kg m-3 ).
calculation: the density of a carbon nucleus(nuclear density)
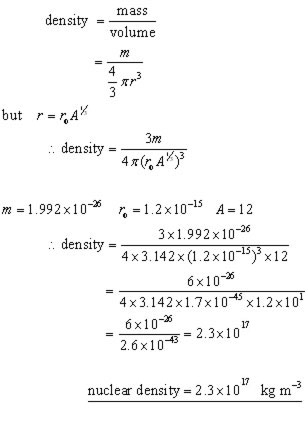
The range of nuclear forces
In all there are four forces that act on matter.
This is the order of their relative strength:
the Strong Force, the Electromagnetic, the Weak and the Gravity force
|
strong |
electromagnetic |
weak |
gravity |
strength |
1 |
7.3 x 10-3 |
10-6 |
6 x 10-39 |
range(m) |
10-15 |
∞ |
10-18 |
∞ |
particle |
mesons, gluons |
photons |
bosons |
gravitons |
notes:
The range of the Strong Force is approximately the diameter of an average nucleus.
The range of the Weak Force is approximately 0.001 the diameter of a proton.
The Weak Force particles are the intermediate vector bosons: W+ W- Zo
[ About ] [ FAQ ] [ Links ] [ Terms & Conditions ] [ Privacy ] [ Site Map ] [ Contact ]
